We closely examine a topic we encounter frequently in daily life; What is a barcode?

03 6 2017
WHAT IS BARCODE?
In addition to standard and commercial uses, as well as bar code, assays and test results performed in hospitals provides information quickly available in the electronic system.
A barcode is a symbol made up of vertical lines and spaces of different thickness. The most common barcode types in the world are EAN-13 and QR Code.
HISTORY OF BARCODE
In 1940, when an American supermarket chain owner asked for a system that allows the information of all the products that pass through the checkout in their markets to quickly record into the system, Bernand Silver began to do research on the subject.
Although Bernand thought of using infrared rays as the first way to use it, he later gave up thinking that this system would be expensive.Continuing his research, Bernand tried to find a solution with a system similar to Morse code and, unlike Morse code, thought to use thin lines instead of dots.
This system was very close to today's barcode system, but they continued to improve the system as the scanner took a long time to read the barcode.Bernard's partner, Norman Woodland, was working at IBM at the time.Working at IBM in the mid-1970s, Woodland, together with George Laurer, who also worked at IBM, developed the 12-digit complex code known as the "Universal Product Code", which was approved in 1973.
The first barcode sale took place on June 26, 1974, at 08:01 am, with a package of chewing gum processed in the cash register of the Marsh Supermarket in Troy, Ohio, USA.

BARCODE TYPES
There are many different types of barcodes used worldwide.Commonly used barcode types are UPC, EAN, EAN-13, EAN-8, Code 39, Code 93, Code 128.The most used ones are UPC and EAN.UPC barcode types in Canada and the United States, the EAN-13 barcode system used in Europe and Turkey.
It was at the end of the 1980s that our country met with the EAN barcode system, our economy opened up and our export products faced problems in terms of labeling and identification in international markets.
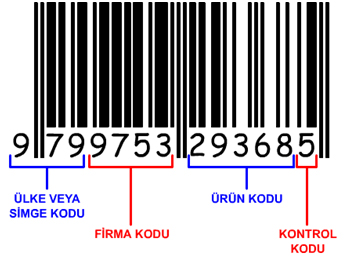 EAN – 13
EAN – 13
The EAN-13 system is a barcode system derived from the UPC system. Since the UPC system is used only in the USA and Canada, it is not suitable for use in international markets. EAN is the abbreviation of the English words "International Article Numbering Association".
According to the declaration published by EAN, after 2005, the EAN will switch to the international barcode system in the USA and Canada. The EAN system is used for the numbering of retail products, especially grocery products. It has also started to be used in the numbering of the Book (ISBN) and periodicals (ISSN). Ean 13 consists of 4 groups and 13 digits.
Country code: The country number issued by Ean. Each country has its own code. Our country's code is 869.
Company code: It is the business number given by the numbering center. It is also called the firm code. It is the 4 digits after the country code. This code TOBB (Union of Chambers and Commodity Exchanges of Turkey) in the body is taken from the Commodity Numbering Center.
Product code: It is the product number given by the enterprise. The product code that comes after the company code consists of 5 digits.
Control code: The last digit of the EAN barcode. It is defined as a control code. This code is the number of checks calculated with a certain formula to prevent other numbers from being read incorrectly.
Calculation of the control code
It checks the accuracy of the lines on the barcode with some mathematical operations during barcode reading of barcode reading devices.
For example; It was passed through a barcode reading device with code 9799753293685.
1. Starting from the far right of the barcode number, all digits are separated in one pair, with the first digit being odd.
2. The numbers in the single digit are added up and multiplied by 3.
3. The numbers in the double digits are added up.
4. Both numbers are added together and the required number is added to reach a multiple of 10.
The barcode reader explains the above steps sequentially after reading the barcode. The barcode scanner machine performs the operations I have described above after reading the barcode. If the control code it found is the same as the one it read, the barcode has been read correctly. If it is incorrect, a warning will be given to be read again.
UPC
UPC is short for "Universal Product Code". It means universal product code. It is the first barcode standard with the widest application. It is used for standard coding of the products offered for sale. The most used types of UPC barcode systems are UPC - A and UPC --E.
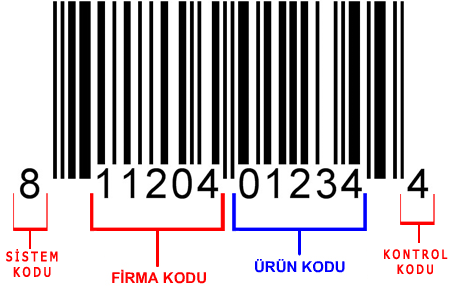
UPC - A
UPC-A consists of 12 digit numeric characters used in the retail industry. UPC-A symbols contain 11 data and 1 control digit number. The first digit is the system number digit and indicates the product registration type.
The following 5 digits are the manufacturer's code. The last 5 digits are used to describe the product. The check digit is calculated and added by the program.
UPC - E
UPC-E is a 7-digit UPC symbology. Used in the small-scale retail industry. In UPC-E barcode symbology, 6 digits are entered, the 7th digit is the control digit.

BENEFITS OF BARCODE
Cost: The system will become more economical as the labor cost will decrease with the increase in accuracy and the increase in data entry speed.
Accuracy: Provides the most accurate information, eliminates user errors. It prevents confusion between similar products or products with similar codes.
Speed: Fast data entry has two important benefits.
1. The requested information is collected quickly and accurately, far above the information to be collected manually.
2. Since this collected correct information is in computer environment, it reaches people or media who can process and evaluate this information very quickly.
For example; Assume that this information is accurately written on a piece of paper. How can you find out how much A brand detergent is sold out of that paper? Yes, you can. What would you do if you were asked at the last minute for all detergent sales, not A brand detergent?
Benefits for producers
- Traceability required by ISO standards can be easily achieved.
- The entry - exit and stock status of the products can be easily monitored.
- It provides convenience in the inspection of the products.
- Quality and control processes are shorter and easier.
- In product orders, stock status is instantly learned and necessary measures are taken.
- Cost is easily followed.
- Shipments are made on time and accurately.
- Labor and space are saved.
- Working efficiency increases.
Benefits for retailers
- The mobility and stock status of the products can be easily monitored.
- Inventory counting takes place quickly and reliably.
- Convenience is provided in the management of the products in the warehouse and in the aisle layout.
- Customers' waiting times are shortened and transactions are accelerated.
- Errors in transactions are reduced and customers' trust is ensured.
- Data can be reached easily in sales statistics.
- Easy to close the safe.
Benefits for distributors and wholesalers
- Inventory counting is done quickly and accurately.
- Movements and stocks of products are easily and instantly monitored.
- Warehouse management is facilitated by easily controlling the movement of the products in the warehouse.
- Costs are reduced by saving labor and space in the enterprise.
- Working efficiency increases in the business.
Benefits to buyers
- Warehouse management is made easy.
- Data is obtained accurately with the arrival time of the products coming to the business.
- Acceleration and accuracy are provided in goods acceptance procedures.
- Fast and accurate information is gained inside and outside the company.
- High productivity in the working environment.
BARCODE SYSTEM
More than 100 GS1 member organizations around the world assist users in the implementation of the barcode system.
The first step in transitioning to the barcode system; It is the collection of numbers to be used on barcodes. These numbers are called "GS1 Identification Keys". In order for a company to produce "GS1 Identification Keys", it must have "GS1 Company Prefix".
Barcode System (GS1 System) is managed by the GS1 organization headquartered in Brussels. GS1 organization, GS1 member Turkey, starting with the prefix 868 or 869 prefixes company serves. Companies use these prefixes to number their products.
The main purpose of the GS1 barcode and numbering system; To increase efficiency and productivity in supply chain management by providing faster and more accurate information transfer to information systems. The reason why GS1 member organizations have different prefixes is not to determine the origin of the products, but to prevent any two numbers used in the world from overlapping each other.
Within the scope of the barcode system, the barcode number given to the products is recommended by the manufacturer, but it is not required; It can be numbered by the product distributor, exporter or even importer. The start of that product with the barcode of a product 868 or 869 is certainly not guaranteed to be produced in Turkey. Importers company, imported products with GS1 company prefix that have taken referring to Turkey does not constitute a disadvantage in terms of GS1 numbering system.
GS1 company prefix in Turkey to receive; https://goo.gl/eJ4K4N

BARCODE PRINTING METHODS
There are multiple ways to print barcode labels in your business. Some of these routes have advantages and some have disadvantages.
1. Barcode printing on laser printer: You can print barcode from laser printers. The laser printer has no service and spare parts problems.
2. Barcode printing in barcode printer: Barcode printing techniques in barcode printer are divided into two as "Direct Thermal" and "Thermal Transfer".
2.1. Direct Thermal Printing
In this method, printing is done by heating the paper. In this method, a heat-resistant paper is heated and burned like in fax machines. With the effect of this heat, the paper turns black and thus the printing process is done. However, environmental factors play an important role in printing made by this method. This printing method is short-lived. Because they are affected by the sun, heat, intense light, and they may deteriorate. But it is ideal for short-term use.
- There is no ribbon expense, it prints by burning.
- Thermal label is used. (Thermal labels are expensive compared to vellum labels.)
- Label life is short. It is suitable for labels that will be consumed in a short time.
- The price of the printer is more economical than direct thermal printer.
2.2. Thermal Transfer Printing
Prints made with this method take longer. In this method, ribbons are used. Here, ribbon takes the place of the heated paper in direct thermal printing. The ribbon is heated and stuck on the paper. It is a healthier and more durable method. It is not directly affected by sun, heat and intense light. It is long-lasting.
- There is a ribbon expense.
- It can print on vellum labels or different labels such as plastic and woven.
- Label life is very long.
- Printer price is more expensive than direct thermal barcode printer. Many direct thermal printers produced recently are also capable of thermal printing. When you buy this type of printer, you have the opportunity to print both ways.

QR CODE
The QR Code was invented by Denso Wave, a subsidiary of the Japanese auto company Toyota. The QR Code, which is widely used in Japan and South Korea, has been developed for use in the automotive industry.
The QR Code takes its name from the initials of the English Quick Response words and usually consists of black motifs on a square white background. It is a special matrix barcode type that can be read from the cameras of mobile devices.
With the impact of the introduction of digital camera mobile phones into our lives, the use of QR Code has become widespread. The most important feature of the QR Code, which makes a fast entrance to our lives and the world of technology, is that it provides a very high speed of information within seconds.
You can access this information immediately with the QR Code Reader application and camera that you will install on your smartphone instead of keeping in mind and note down the article, advertisement, website address or contact information that attracts your attention in a shopping mall, on a magazine page, on a billboard or anywhere. , you can record it and use it whenever you want.

One of the different uses of the QR Code is the tombstone. It is possible to reach the life stories of the people who lost their lives and all the photos taken throughout their lives by bringing your phone closer and reading the QR Code. This method, which is mostly used on popular people such as artists, politicians, actors, activists, who have left a mark in the world history, is a different use of QR Code.
For example, the tombstone you see in the photo; It belongs to Nelson Mandela, the first black president of the Republic of South Africa.
Differences of QR Code compared to traditional barcode
1. QR Code size can be as small as 1/10 of traditional bar codes.
2. QR Code can be read from all directions according to classical barcode types. Scanning feature from all directions enables the QR Code to be read faster.
3. QR Code has error correction feature compared to classic barcode types. It is readable even in case of any soiling or damage on it up to 30%.
Advantages of the QR Code
- The main purpose targeted with Karekod is to reach information faster and more practically thanks to mobile devices.
- QR Code can contain much more letters and numbers.
- It has the opportunity to be used up to 1/10 of the classical barcodes.
- High scanning speed,
Selectable and readable from every angle
- QR codes that are dirty or corrupted to a certain extent can be read.
Data capacity of the QR Code
Numeric up to 7,090 characters
- Alphanumeric up to 4,291 characters
- Maximum 2,953 bytes in binary (8 bit)
- Up to 1,817 characters as Kanji / Kana